In addition to further research and development by screen casting solution providers, wireless screen casting technology has had three built-in screen casting protocols for mobile terminals from the beginning, namely AirPlay, Miracast, and DLAN. Mobile terminals of different brands or operating systems support corresponding screen casting protocols. Different protocols have different characteristics, let’s compare and analyze them below.
【AirPlay】
AirPlay is a wireless technology developed by Apple that can wirelessly transmit images, audio, and videos from iOS devices such as iPhone, iPad, and iPod touch to AirPlay enabled devices through WiFi. The Apple TV priced at $99 already has this feature, and some traditional home theaters and network players now support AirPlay.
AirPlay supports mirroring function, which can wirelessly project images from iPhone or iPad onto TVs that support the AirPlay protocol, meaning that the mobile terminal displays whatever TV screen is large. The mirroring function of AirPlay is supported by DLAN.
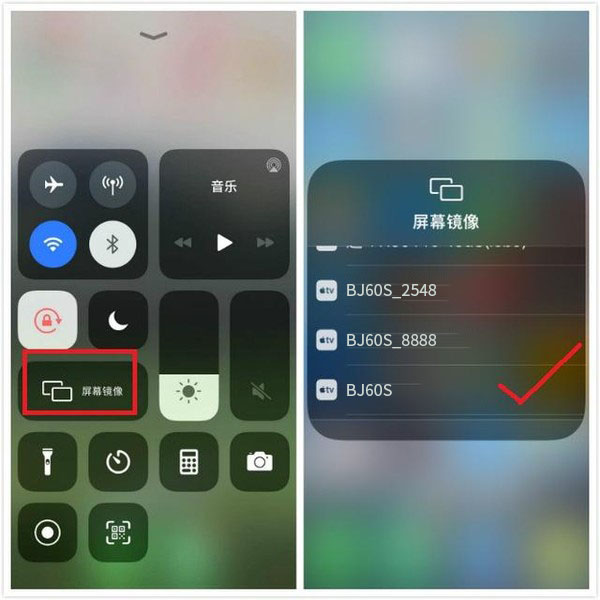
At present, Apple’s AirPlay is mainly applicable to certified Apple devices. Currently, Apple’s own devices, including iPads, iPhones, Apple TVs, etc., support this technology, and some Apple authorized partner devices also support the AirPlay protocol.
Condition: The Apple device and TV are on the same local area network.
Advantages: Wireless screen projection; The native screen mirroring protocol that comes with Apple devices has strong anti-interference capabilities and supports screen mirroring. The mirror effect of AirPlay is the best among all screen projection methods.
Shortcomings: AirPlay is a native screen projection protocol for iOS systems, and its usage is generally limited to Apple devices. Although the AirPlay screen mirroring protocol has been compatible with a small number of screen mirroring devices in the market, it is still not compatible with most screen mirroring devices in the market.
【Miracast】
Miracast is a wireless projection protocol developed by the Wi Fi Alliance in 2012, based on WiFi direct connection. Devices that support this protocol can share video footage through screen mirroring. For example, on the basis that both mobile phones and TVs support the Miracast protocol, movies or photos on mobile phones can be played directly on TVs through the Miracast protocol without being limited by connecting cables.
Unlike DLNA, Miracast also has a mirroring function similar to AirPlay, which can directly project screen content from the phone to the high-definition TV screen. After Android version 4.2, the system comes standard with this protocol (which can be found in the settings or display menu, with application names such as Wlan display Wifi display、Miracast、Allshare cast、Mirroring screen、 Wireless display, etc. (different phone brands have different names), can wirelessly project the screen content of mobile terminals to large screen display devices, such as living room TVs, conference room projectors, etc. through wireless projection receivers. The transmission delay of screen projection using Miracast protocol is below 150ms. This protocol requires the assistance of a wireless screen casting receiver to complete the screen casting operation.
Condition: Both the mobile phone and TV need to support Miracast projection protocol, and the mobile phone and TV need to be in the same local area network; The Miracast setting on the TV is turned on.
Advantages: Wireless screen projection; It is the most widely compatible screen projection protocol, and most mobile phones and smart TVs in China support the Miracast screen projection protocol.
Shortcomings: Some TVs cannot adjust the image mode, and there is a significant color difference between the phone screen and the TV screen.
【DLNA】
DNLA,Digital Living Network Alliance, It is a set of protocols initiated by Sony, Intel, Microsoft, and others for interconnectivity between PCs, mobile devices, and consumer electronics. Their purpose is to “enjoy music, photos, and videos anytime, anywhere.”.
DLNA is similar to Apple’s AirPlay in that it allows media content from your phone to be delivered to the TV screen. The difference is that DLNA on mobile phones does not have a screen mirroring function similar to AirPlay or Miracast. Currently, DLNA only supports projecting photos and videos from mobile phones to large screens.
In addition, online videos can also be pushed to the living room TV for display using DLNA mode. Some players on the Android system have DLNA function. Currently, video clients that support wireless push include Tencent Video, Sohu Video, and PPTV Video, which can project movies from the original phone screen to the TV screen for playback. The prerequisite is that the TV or TV box supports DLNA.
The difference between DLNA and Miracast during launch
DLNA is file based, and media files may have various encoding formats. The player must be able to handle these multiple encoding formats. Usually, for a better playback experience, DLNA will cache for a short period of time.
Miracast is real-time and can transmit the output of the source in real time. Any screen operation on the source end will be transmitted to the receiving (Sink) end. If the source end is playing media files, the source end is responsible for decoding the media files first, and then encoding them into H.264 format. The receiving end only needs to perform H.264 decoding. Therefore, compared to DLNA, Miracast has higher requirements for WiFi access.
Condition: The phone and TV need to support the DLNA screen projection protocol, and the phone and TV are in the same local area network; The DLNA setting of the TV is turned on.
Advantages: Wireless push; Online video push has the best effect.
Shortcomings: can only push online videos; You need to first turn on the TV projection device, and then start DLNA related applications on your phone, so that you can recognize the TV device on your phone.