How to project the screen onto the monitor with the Mac?
With the continuous development of technology, screen projection technology has become an indispensable part of our lives. When we need to transfer images from Mac computers to the monitor, screen mirroring technology provides a convenient way. Below, we will provide a detailed introduction to how Mac projects screens onto monitors, helping you understand different types of screen projection technologies and how to achieve the best screen projection results.
Screen projection technology refers to the technology of transferring the image from one device to another device for display. On Mac computers, common screen projection technologies include AirPlay, DLNA, Miracast, and more. These technologies each have their own characteristics and are suitable for different scenarios and needs.
AirPlay
AirPlay is a wireless projection technology launched by Apple, suitable for Mac and iOS devices. Through AirPlay, you can stream audio, video, and photos from your Mac to devices that support AirPlay, such as Apple TVs, smart TVs, and more.
DLNA
DLNA (Digital Living Network Alliance) is an open projection technology standard that supports multiple device platforms, including Mac. Through DLNA, you can stream music, video, and images from your Mac to DLNA enabled devices such as smart TVs, Blu ray players, and more.

Miracast
Miracast is a wireless projection technology that supports Android and Windows devices. Through Miracast, you can transfer images from your Mac to a Miracast enabled TV or projector.

How to achieve Mac screen projection to the monitor
The following steps are required to implement screen projection to the monitor on Mac:
Connecting the monitor
Firstly, connect the monitor to the Mac computer. If the monitor supports HDMI or VGA interfaces, you can directly use the corresponding cable connection. If the monitor supports wireless connection, you can choose to use Wi Fi or Bluetooth connection.
Open the screen projection software
On a Mac, you can open the built-in screen mirroring software (such as AirPlay or DLNA) or download third-party screen mirroring software. These software can help you transfer images from your Mac to your monitor.
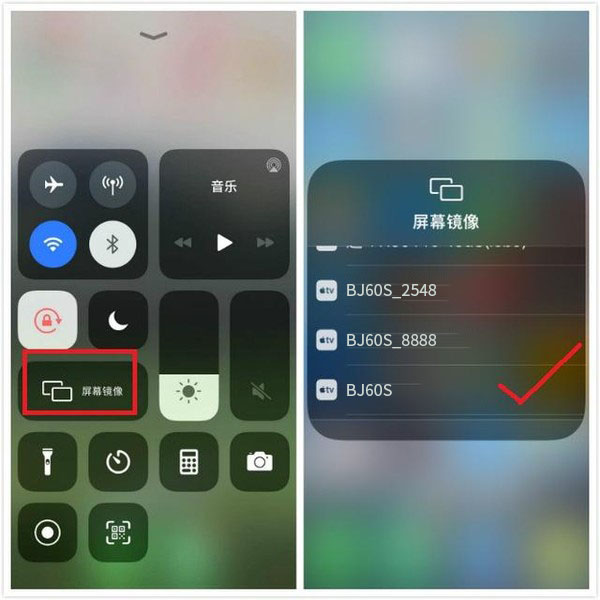
Search for connected devices
After opening the screen projection software, you can search for devices that can be connected. If your monitor supports AirPlay or DLNA, you can see the corresponding device options in the software. Select the device you want to connect to and click Connect.
Adjusting Display Settings
After the connection is successful, you can adjust the picture resolution, color and other parameters in the display settings to ensure the best picture quality. In addition, you can also adjust audio settings as needed to transfer audio streams to audio devices that support AirPlay or DLNA.
Start screen casting
After adjusting the display settings, you can start projecting the screen. Open the software or video file that needs to be projected on a Mac computer, select full screen mode to transfer the image to the monitor. If you need to adjust the screen size or position, you can use the mouse or keyboard for operation.
Common problems and solutions
When using screen projection technology, you may encounter some common problems. Here are some solutions to common problems:
1. Unable to search for connected devices:
Please ensure that your monitor supports AirPlay or DLNA, and check if the device is already connected to the same Wi Fi network. If the devices are not on the same network, you can connect by manually entering the device’s IP address.
2. Unstable connection:
The unstable connection may be caused by network issues or device compatibility. Please try restarting the device or changing the network environment to resolve the issue. If the problem persists, please check if the device is compatible with AirPlay or DLNA protocols.
3. Poor image quality:
If the image quality is poor, you can try adjusting the parameters in the display settings, such as resolution, color, etc. Additionally, please ensure that your Wi Fi network speed is fast enough to support high-quality image transmission.